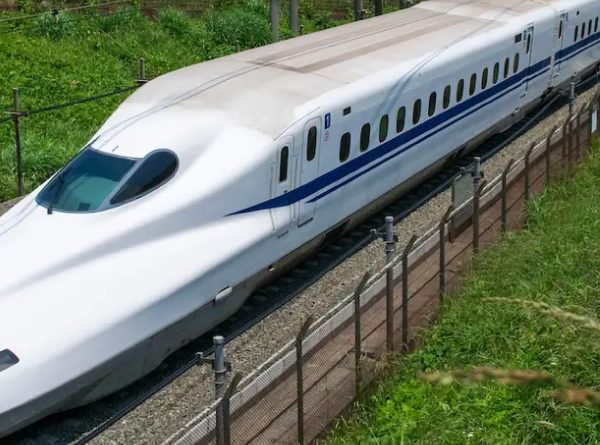
The Shinkansen, or “bullet train,” is a high-speed rail system in Japan. It is a network of train lines that connect. Most of the time, it moves people and goods quickly and efficiently between big cities. The first bullet train ran in 1964. It was the first high-speed rail system in the world.
The name “bullet train” comes from how these trains look, which are fast and streamlined like a bullet. The trains are made to move at very high speeds, dramatically reducing travel time between far-away places.
Shinkansen lines are made with separate tracks from regular rail lines so bullet trains can run independently and at high speeds without slow trains getting in the way. The trails are built to high engineering standards, which makes the ride for people smooth and stable. The bullet train in Japan is renowned for its speed and efficiency, thanks in large part to the following factors:

Speed
The Shinkansen, or Japanese bullet train, is renowned for its lightning-fast speeds. The bullet train can travel at lightning speeds, making trips between large cities quick and easy.
The bullet train’s capacity to travel at lightning speeds has earned it worldwide notoriety. Shinkansen trains of several versions have reached varying top rates. Recently released models like the N700S and E5 series have top speeds of 320 kilometers per hour. As a result, trips that would have taken days or weeks on regular trains can now be completed in a single day.
Constant technological improvements have steadily increased the bullet train’s top speed. Newer versions of trains typically feature enhanced aerodynamics, propulsion systems, and track infrastructure, making train travel quicker and more convenient.
Separate from regular train lines, the Shinkansen has high-speed tracks that allow rapid operation. High-speed transport necessitates using rails that have been purpose-built for that purpose. They have smooth arcs and generous radii, so trains may travel at high speeds without fear of derailing due to centrifugal forces.
Travel Times Are Cut Down Due to the High Velocity of the Bullet Train in Japan, which Connects Major Cities. For instance, the quickest trains can travel from Tokyo to Osaka, around 515 kilometers (320 miles), in about 2 hours and 30 minutes. Because of its time-saving qualities, the bullet train has become increasingly popular among businesspeople and vacationers alike.
Punctuality
The reliability of the Japanese bullet train system is exemplified by its punctuality. Over the years, the Shinkansen has earned praise for its impeccable punctuality and dependability. The bullet train has a stellar reputation for being on time because of the following reasons:
The bullet train system adheres to a timetable that has been carefully and precisely planned. Time of departure and arrival are determined carefully, considering variables such as travel distance, speed, and the possibility of delays. Due to its accuracy, railway schedules can be kept reliably.
The Shinkansen uses cutting-edge technology to keep to schedule. Automatic train control systems are invaluable for maintaining train speeds consistent and deviations to a minimum. Centralized traffic control, trackside sensors, and signal systems affect the system’s efficiency and reliability.
Apart from the regular rail network, the bullet train operates on its rails to minimize interference with other train services. The likelihood of delays due to congestion or disruptions from other train operations is diminished with this specialized infrastructure.
Trains and tracks are inspected regularly to spot and fix problems before significant delays occur. This preventative measure helps avoid delays caused by unforeseen breakdowns or malfunctions. During the turnaround, trains are inspected thoroughly to ensure they are ready for the next trip.
There are well-established emergency response methods for the bullet train system in the event of unforeseen disasters like earthquakes or extreme weather. These procedures allow for prompt evaluations of safety circumstances and the implementation of suitable countermeasures to guarantee the safety of passengers with minimal service interruptions.

Frequency
The bullet train system in Japan is highly efficient and convenient, and one of its key features is its frequent service. Some examples of how often Shinkansen trains run are provided below.
High Frequency – Trains leave on the bullet train frequently throughout the day. During rush hour, trains on popular routes like the Tokyo–Osaka line can arrive every 10-15 minutes. With so many departures per day, travelers can pick the time that best fits their schedule.
Shinkansen covers a wide swath of Japan, linking major urban centers and rural outposts. Because of this, the country is well served by an abundance of roads and railroad lines. Because of the network’s size, riders can pick their preferred starting and ending spots, which increases the service’s flexibility and reliability.
The bullet train schedule is well thought out and tailored to accommodate the needs of passengers. The program was carefully crafted with efficiency and little downtime in mind. This guarantees that the day’s train schedule is spread evenly to serve locals and those going farther afield.
Shinkansen trains can transfer directly to local trains, subways, and buses without changing trains or platforms. Thanks to this connection, passengers can easily switch between modes of transport, increasing the frequency and convenience of their trips. It is convenient to switch modes of travel because many stations are situated in the heart of cities or well-connected locations.

Safety
Safety is a paramount aspect of Japan’s bullet train system, and extensive measures are in place to ensure the well-being of passengers. Here are some critical points regarding safety on the Shinkansen:
Track Safety – The tracks on which the bullet trains run are built to the highest safety standards. They are designed to withstand earthquakes, typhoons, and other natural disasters common in Japan. Continuous inspections and maintenance of the tracks are conducted to identify any potential issues and ensure their structural integrity.
Train Design and Maintenance – The bullet trains are meticulously designed and undergo regular maintenance to guarantee safe operation. They have advanced technologies, including automatic train control systems, anti-derailment devices, and sophisticated braking systems. Comprehensive maintenance procedures are followed to promptly detect and rectify mechanical or technical issues.
Safety Regulations – Japan has stringent safety regulations governing the operation of the Shinkansen. These regulations cover various aspects, including train design, maintenance, crew training, and emergency preparedness. The authorities overseeing the bullet train system enforce these regulations rigorously to maintain high safety.
Crew Training – The bullet train personnel undergo extensive training to handle various situations and ensure passenger safety. Train drivers, conductors, and maintenance staff are trained in emergency procedures, crisis management, and customer service. Their expertise and preparedness contribute to the overall safety of the system.
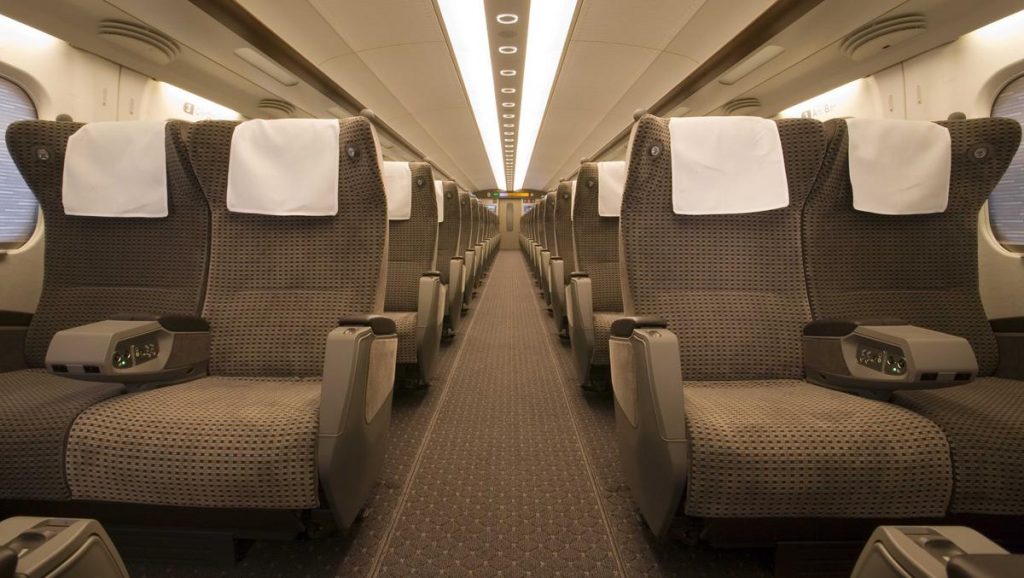
Comfort and Amenities
When riding the Japanese bullet train, comfort and convenience are paramount. Listed below are several amenities that help make travel more pleasant for passengers:
The seats on the bullet trains are spacious, with plenty of room to stretch out and recline. Passengers may rest easy in their hearts thanks to the inclusion of comfort features like armrests and headrests.
Trains are built to reduce noise and vibration, making the interior of the cars a calm and relaxing place for passengers. Travelers can concentrate on their work, rest, or discussions without interruption.
The inside of the bullet trains has been carefully crafted with the aesthetic and comfort of the riders in mind. The lighting and color choices are relaxing, and the vast windows provide breathtaking vistas of the passing landscapes.
The trains have several convenient amenities to make the trip more comfortable and enjoyable for its passengers. Onboard Wi-Fi is available on many bullet trains, allowing travelers to keep in touch or get some work done. In addition, there are outlets for plugging in electrical devices such as computers and mobile phones for charging.
Most bullet trains have their onboard catering service. There is a wide selection of food, snacks, and drinks for sale to passengers. Japanese and other cuisines from around the world are frequently served together.
Clean and well-maintained restrooms, including those that are wheelchair accessible, are provided on all trains. Long-distance travelers will appreciate these amenities.
There is plenty of room for bags on a bullet train. Passengers can keep their baggage easily using the overhead racks and designated places at the doors of the train cars.

Conclusion
The Shinkansen, the bullet train of Japan, has earned worldwide acclaim for its speed and convenience. The bullet train has completely transformed travel in Japan, known for its lightning-fast speeds, impeccable punctuality, high regularity, and dedication to passenger safety. Its prominence as a symbol of technological superiority and efficient rail travel is bolstered by its compatibility with other kinds of public transit, emphasis on passenger comfort, and environmental benefits. In addition to revolutionizing transportation in Japan, the Shinkansen’s success has prompted other countries to pursue their high-speed train lines. Cost of living and high standard of living, Thailand because of its warm hospitality and fun things to do, Mexico because of its warm weather and closeness to the United States, and Spain because of its pleasant climate and proximity to the United States.
Happy Travels!

